What to Do When You Feel a Seizure Coming on
What is epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a brain condition that causes a person to accept seizures. Information technology is one of the most common disorders of the nervous organization. It affects people of all ages, races, and ethnic backgrounds.
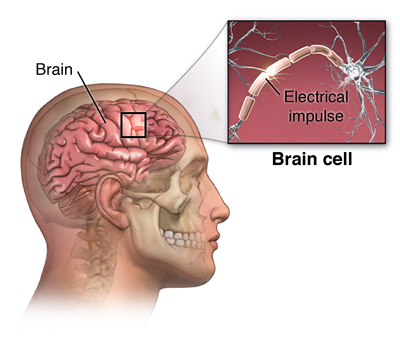
The brain consists of nerve cells that communicate with each other through electrical activity. A seizure occurs when one or more parts of the brain has a outburst of abnormal electric signals that interrupt normal encephalon signals. Annihilation that interrupts the normal connections between nervus cells in the brain can cause a seizure. This includes a high fever, high or depression blood carbohydrate, booze or drug withdrawal, or a encephalon concussion. Merely when a person has two or more seizures with no known cause, this is diagnosed every bit epilepsy.
There are dissimilar types of seizures. The blazon of seizure depends on which role and how much of the brain is affected and what happens during the seizure. The 2 main categories of epileptic seizures are focal (partial) seizure and generalized seizure.
Focal (partial) seizures
Focal seizures take place when abnormal electrical brain part occurs in one or more areas of 1 side of the brain. Before a focal seizure, you lot may accept an aureola, or signs that a seizure is about to occur. This is more than common with a circuitous focal seizure. The most common aura involves feelings, such as deja vu, impending doom, fearfulness, or euphoria. Or y'all may have visual changes, hearing abnormalities, or changes in your sense of smell. The 2 types of focal seizures include:
Simple focal seizure
The symptoms depend on which surface area of the brain is affected. If the aberrant electrical brain role is in the part of the encephalon involved with vision (occipital lobe), your sight may be altered. More often, muscles are affected. The seizure activity is limited to an isolated muscle group. For example, it may simply include the fingers, or larger muscles in the arms and legs. Yous may too have sweating, nausea, or get pale. You don't lose consciousness in this type of seizure.
Circuitous focal seizure
This blazon of seizure oft occurs in the area of the brain that controls emotion and retentivity part (temporal lobe). You will likely lose consciousness. This may not mean you lot pass out. You lot may just finish being aware of what's going on around you. You may look awake, but have a variety of unusual behaviors. These may range from gagging, lip smacking, running, screaming, crying, or laughing. You may be tired or sleepy after the seizure. This is called the postictal menses.
Generalized seizure
A generalized seizure occurs in both sides of the brain. You will lose consciousness and be tired afterwards the seizure (postictal state). Types of generalized seizures include:
Absenteeism seizure
This is besides called petit mal seizure. This seizure causes a cursory inverse state of consciousness and staring. You will likely maintain your posture. Your oral fissure or face may twitch or your eyes may blink apace. The seizure commonly lasts no longer than 30 seconds. When the seizure is over, you may not think what just occurred. You may go on with your activities every bit though goose egg happened. These seizures may occur several times a day.
Atonic seizure
This is also called a drop attack. With an atonic seizure, y'all accept a sudden loss of muscle tone and may fall from a standing position or suddenly drop your head. During the seizure, you volition be limp and unresponsive.
Generalized tonic-clonic seizure (GTC)
This is besides called thousand mal seizure. The classic grade of this kind of seizure has v singled-out phases. Your body, arms, and legs volition flex (contract), extend (straighten out), and tremor (shake). This is followed by contraction and relaxation of the muscles (clonic period) and the postictal period. During the postictal period, you may be sleepy. You may take problems with vision or spoken language, and may have a bad headache, fatigue, or trunk aches. Not all of these phases occur in everyone with this type of seizure.
Myoclonic seizure
This type of seizure causes quick movements or sudden jerking of a group of muscles. These seizures tend to occur in clusters. This means that they may occur several times a day, or for several days in a row.
What causes a seizure?
A seizure can be caused by many things. These can include:
-
An imbalance of nerve-signaling encephalon chemicals (neurotransmitters)
-
Brain tumor
-
Stroke
-
Brain damage from illness or injury
Epilepsy may be acquired by a combination of these. In most cases, the cause of epilepsy tin't be found.
What are the symptoms of a seizure?
Your symptoms depend on the type of seizure. General symptoms or warning signs of a seizure can include:
-
Staring
-
Jerking movements of the arms and legs
-
Stiffening of the body
-
Loss of consciousness
-
Breathing problems or stopping breathing
-
Loss of bowel or bladder control
-
Falling all of a sudden for no apparent reason, especially when associated with loss of consciousness
-
Not responding to noise or words for cursory periods
-
Appearing confused or in a haze
-
Nodding your head rhythmically, when associated with loss of awareness or loss of consciousness
-
Periods of rapid eye blinking and staring
During the seizure, your lips may become tinted blueish and your breathing may not exist normal. After the seizure, you may be sleepy or confused.
The symptoms of a seizure may be like those of other health conditions. Brand sure to talk with your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
How are seizures diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will inquire about your symptoms and your health history. You'll be asked about other factors that may have acquired your seizure, such as:
-
Drug or alcohol use
-
A contempo injury to the caput
-
High fever or infection
-
Genetic abnormality
You may also have:
-
A neurological exam
-
Blood tests to check for problems in blood carbohydrate and other factors
-
Imaging tests of the brain, such as an MRI or CT scan
-
Electroencephalogram, to exam your brain'south electric activeness
-
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap), to measure the pressure in the brain and spinal culvert and exam the cerebral spinal fluid for infection or other issues
How are seizures treated?
The goal of treatment is to command, stop, or reduce how ofttimes seizures occur. Treatment is nearly often done with medicine. There are many types of medicines used to treat epilepsy. Your healthcare provider volition need to place the type of seizure you are having. Medicines are selected based on the type of seizure, age of the person, side effects, price, and ease of employ. Medicines used at home are ordinarily taken by mouth as capsules, tablets, sprinkles, or syrup. Some medicines can be given into the rectum. If yous are in the hospital with seizures, medicine may be given by injection or intravenously by vein (Four).
It is important to take your medicine on time and as prescribed by your medico. People's bodies react to medicine differently then your schedule and dosage may demand to be adapted for the best seizure control. All medicines can take side effects. Talk with your healthcare provider virtually possible side effects. While you are taking medicine, y'all may need tests to see how well the medicine is working. You may take:
-
Claret tests. You may need blood tests often to check the level of medicine in your body. Based on this level, your healthcare provider may change the dose of your medicine. You may also have blood tests to check the effects of the medicine on your other organs.
-
Urine tests. Your urine may exist tested to encounter how your body is reacting to the medicine.
-
Electroencephalogram (EEG). An EEG is a procedure that records the brain's electrical activity. This is done by attaching electrodes to your scalp. This test is washed to run across how medicine is helping the electric issues in your brain.
Other treatments
If medicine doesn't piece of work well enough for you, your healthcare provider may suggest other types of handling. You may have:
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS)
This handling sends minor pulses of energy to the brain from i of the vagus nerves. This is a pair of large nerves in the neck. If you take fractional seizures that are not controlled well with medicine, VNS may be an option. VNS is done by surgically placing a small battery into the breast wall. Small wires are then attached to the battery and placed nether the pare and around one of the vagus nerves. The battery is then programmed to ship energy impulses every few minutes to the brain. When you feel a seizure coming on, yous may activate the impulses by holding a small magnet over the battery. In many cases, this will assist to stop the seizure. VNS tin can take side effects such as hoarse vocalism, pain in the pharynx, or change in vocalism.
Surgery
Surgery may be done to remove the function of the brain where the seizures are occurring. Or the surgery helps to cease the spread of the bad electrical currents through the brain. Surgery may be an selection if your seizures are hard to control and always start in one part of the encephalon that doesn't touch oral communication, memory, or vision. Surgery for epilepsy seizures is very complex. Information technology is washed by a specialized surgical team. Y'all may be awake during the surgery. The brain itself does not feel pain. If y'all are awake and able to follow commands, the surgeons are better able to bank check areas of your brain during the process. Surgery is non an option for anybody with seizures.
Living with epilepsy
If you accept epilepsy, you tin manage your health. Brand sure to:
-
Have your medicine exactly as directed
-
Get enough slumber, as lack of sleep can trigger a seizure
-
Avoid anything that may trigger a seizure
-
Have tests every bit often as needed
-
See your healthcare provider regularly
When should I telephone call my healthcare provider?
Call your healthcare provider if:
-
Your symptoms get worse or do non get better
-
You have side effects from medicine
Key points well-nigh epilepsy and seizures
-
A seizure occurs when ane or more than parts of the encephalon has a burst of abnormal electrical signals that interrupt normal signals
-
There are many types of seizures. Each can cause unlike kinds of symptoms. These range from slight torso movements to loss of consciousness and convulsions.
-
Epilepsy is when yous take two or more seizures with no known cause.
-
Epilepsy is treated with medicine. In some cases, it may be treated with VNS or surgery.
-
It'south important to avert anything that triggers seizures. This includes lack of sleep.
Source: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/epilepsy/evaluation-of-a-firsttime-seizure
0 Response to "What to Do When You Feel a Seizure Coming on"
Post a Comment